Lasers for Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called “single-beam gradient force trap”) are a bioanalytical instrument that makes use of a highly-focused laser beam to provide an attractive or repulsive force, depending on the refractive index mismatch to physically hold and move microscopic dielectric objects. Optical tweezers have become a well known and successful tool in studying a variety of biological systems.
The narrowest point of the focused beam, known as the beam waist, contains a very strong electric field gradient. It turns out that dielectric particles are attracted along the gradient to the region of strongest electric field, which is the center of the beam. The laser light also tends to apply a force on particles in the beam along the direction of beam propagation. By utilising this force it is possible to manipulate biological cells and even move them from one position to another.
A basic optical tweezer setup includes:
a laser, a beam expander, some optics used to steer the beam location in the sample plane, a microscope objective and condenser to create the trap in the sample plane, a position detector (e.g. quadrant photodiode) to measure bea m displacements an d a microscope illumination source coupled to a CCD camera (see Fig.1 on the right). All Cobolt DPSS lasers offer excellent beam quality and very low noise, which are extremely important properties of lasers used for optical tweezers.
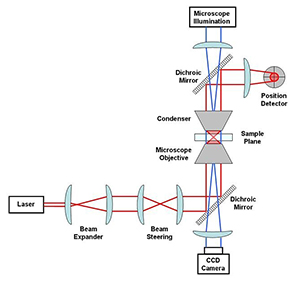
Fig 1: Basic optical tweezer setup
See related products

Cobolt 04-01 Series
Single frequency, CW diode pumped lasers
Wavelength: 457 nm – 1064 nm
Power: 25 mW – 400 mW
Applications: Raman, microscopy, LDV, DLS

Cobolt 05-01 Series
High power, single frequency, CW diode pumped lasers
Wavelength: 320 nm – 1064 nm
Power: 10 mW – 3000 mW
Applications: Holography, Raman, microscopy, flow cytometry, research

Cobolt 06-01 Series
Plug & play modulated CW lasers
Wavelength: 375 nm – 1064 nm
Power: 40 mW – 400 mW
Applications: Microscopy, flow cytometry, optogenetics

